CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers V3.1
1. A router determines the path to deliver a packet. What layer of the OSI model does this fact represent?
session
transport
network
data link
physical
2.
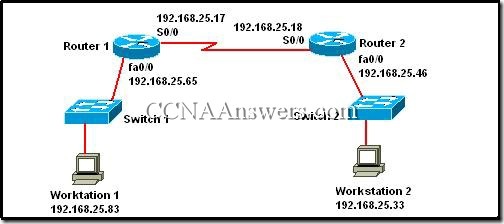
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured a network after subnetting the network number 192.168.0.0/28. Workstation 1 is not able to communicate with Workstation 2. What is the cause of this loss in communications?
Workstation 1 and Workstation 2 are on the same subnet.
The serial connections are using addresses from the LAN subnets.
Workstation 1 is not on the same network that the Router 1 LAN interface is on.
If routers are used in the network, IP addresses do not need to be subnetted.
3. Which physical network topology is easy to monitor and troubleshoot, easy to add new devices to as the network expands, but subject to complete failure when a central hub or switch ceases to work?
bus
star
ring
mesh
4.
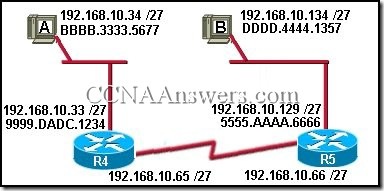
Refer to the exhibit. Host A pings Host B. What can be concluded about the source and destination addresses contained in the communication sent by Router R5 when it forwards the ping out the Ethernet interface to Host B? (Choose two.)
source IP address: 192.168.10.129
source MAC address: BBBB.3333.5677
source MAC address: 5555.AAAA.6666
destination IP address: 192.168.10.33
destination IP address: 192.168.10.134
destination MAC address: 9999.DADC.1234
5. Which network device creates the highest amount of latency?
hub
router
switch
bridge
6.
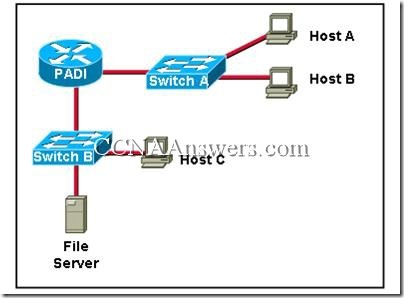
Refer to the exhibit. What must be configured on Host B to allow it to communicate with the file server? (Choose three.)
the MAC address of the file server
the MAC address of the PADI router interface connected to Switch A
the IP address of Switch A
a unique host IP address
the subnet mask for the LAN
the default gateway address
7. A computer technician is asked to make a network cable. One end of the cable is pinned as a 568A and the other as a 568B. For what purposes can this cable be used? (Choose two.)
to connect a router to a switch
to connect a switch to a switch
to connect a host to a switch
to connect a hub to a switch
to connect a router to a hub
to connect a host to a hub
8. When using Category 5 UTP cable, which RJ-45 pin pairs are used to exchange data between hosts on an Ethernet network?
1 and 2; 4 and 5
1 and 2; 3 and 6
3 and 6; 7 and 8
4 and 5; 7 and 8
9. What is the correct number of usable subnetworks and hosts for the IP network address 192.168.35.0 subnetted with a /28 mask?
6 networks / 64 hosts
14 networks / 32 hosts
14 networks / 14 hosts
30 networks / 64 hosts
10. Which devices will create multiple collision domains in an Ethernet network? (Choose two.)
NIC
hub
switch
router
repeater
11. What is the decimal representation of the binary number 11111000?
224
240
248
252
254
12. Which characteristics are common to both UDP and TCP? (Choose two.)
provides windowing
provides reliability
uses port numbers
acknowledges receipt of data
classified as a connectionless protocol
classified as a transport layer protocol
13. The ping command can be used to test connectivity between hosts. Which OSI model layers are verified by this test?
Layers 1 and 2 only
Layers 1 and 3 only
Layers 1, 2 and 3
Layer 1 through Layer 7
Layer 4 through Layer 7
14. Why do vendors utilize the OSI model when designing networking products?
It places requirements on all vendors that develop proprietary networking technologies for advance networking systems.
It ensures greater compatibility and interoperability with equipment from different vendors.
The International Organization for Standards develops all new products to be incorporated into the product.
It is mandated by the International Organization for Standardization that network products be compliant with the OSI model.
15. An Ethernet host receives a frame, calculates the FCS, and compares the calculated FCS to the FCS received in the frame. The host finds that the two FCS values do not match. What action will be taken by the host?
The host discards the frame.
The host processes the data frame normally.
The host initiates a request for retransmission of the frame.
The host sends the frame content to an upper layer protocol for error recovery.
16. Why would a company install a switch instead of a hub when building or expanding a corporate network?
A switch manages frames faster than a hub does.
A switch operates at 100 Mbps. A hub operates at a maximum of 10 Mbps.
A switch modifies the Ethernet frame to remove any errors. A hub forwards the frame exactly as it arrived.
A switch provides more bandwidth by sending frames only out the port to which the destination device is attached. A hub sends the frame out all ports except the source port.
17.
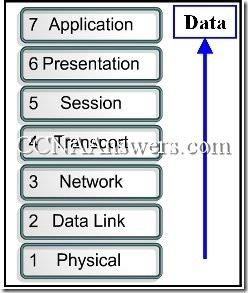
Refer to the exhibit. What is the order of the TCP/IP Protocol Data Units as data is moved as indicated through the OSI model?
bits, segments, frames, packets, data
bits, frames, packets, segments, data
bits, frames, segments, packets, data
bits, packets, frames, segments, data
18. After an unsuccessful ping to the local router, the technician decides to investigate the router. The technician observes that the lights and fan on the router are not operational. In which layer of the OSI model is the problem most likely occurring?
transport
network
data link
physical
19. Which of the following statements are correct about CSMA/CD? (Choose three.)
It is a media access method used in LANs.
It is a media access method used in FDDI WANs.
When a device needs to transmit, it checks to see if the media is available.
A device sends data without checking media availability because all devices have equal access.
Multiple devices can successfully transmit simultaneously.
Only one device can successfully transmit at a time.
20. A network administrator has installed a 24 port switch and connected 10 computers with 10/100 NICs. If the NICs are operating at 100 Mbps, how much bandwidth is available for each computer to receive data?
0.24 Mbps
4.17 Mbps
10 Mbps
24 Mbps
100 Mbps
200 Mbps
21.

Refer to the exhibit. A newly hired technician has a task of terminating CAT 5 UTP cables. The network administrator visually examined the cables the technician terminated. Some of the cables have connectors as shown in the exhibit. What should the network administrator explain to the technician about the cables?
Both cables are acceptable.
The cable in Graphic A will produce more crosstalk.
The cable in Graphic A should be used in the more critical network segments.
The cable in Graphic A is preferred because it will be easier to crimp the connector.
22. Which technologies are considered to be LAN technologies? (Choose two.)
DSL
Token Ring
Frame Relay
ISDN
Ethernet
23.
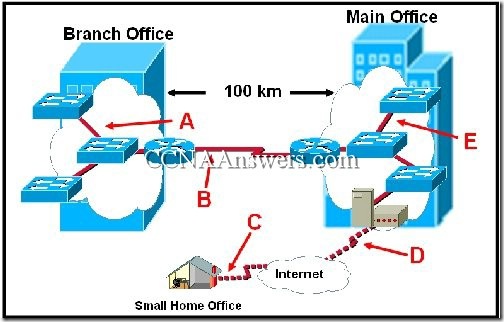
Refer to the exhibit. The connections in the exhibit are labeled A through E. Which of these indicate LAN links? (Choose two.)
link A
link B
link C
link D
link E
24.
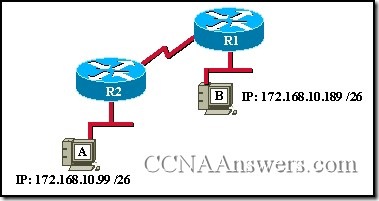
Consider the networks shown in the exhibit. Host A is sending packets to host B. Which layer of the OSI model is being used when the router is making the calculated decision to determine which interface to send the packet out?
physical
data link
network
transport
session
presentation
25. What are important characteristics to consider when purchasing a network interface card? (Choose two.)
security used on the network
media used on the network
system bus used on the computer
software installed on the network
diagnostic tools installed on the network
26.
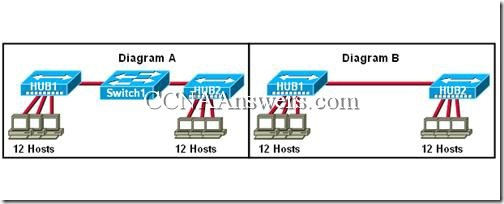
Refer to the exhibit. Which diagram represents the network topology that an administrator would prefer, and why would the administrator prefer it?
Diagram A. It provides the hosts with full-duplex connections.
Diagram A. It will better provide available bandwidth to the hosts.
Diagram B. It extends the collision domain.
Diagram B. It prevents the frames from looping.
Either network will perform equally well.
27.
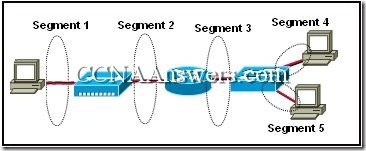
Refer to the exhibit. The physical documentation shows a portion of the internetwork of the ABC Company. Which segments will be free of collisions?
segments 1 and 2
segments 1, 2, and 3
segments 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
segments 2 and 3
segments 3, 4, and 5
segments 4, and 5
28.

Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator wants to create a subnet for the point-to-point connection between the two routers. Which subnetwork mask would provide enough addresses for the point-to-point link with the least number of wasted addresses?
255.255.255.192
255.255.255.224
255.255.255.240
255.255.255.248
255.255.255.252
29.
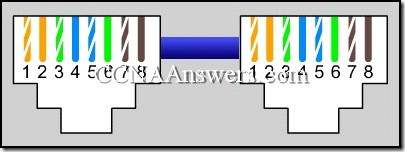
Refer to the exhibit. What kind of Ethernet cable is represented?
rollover cable
straight-through cable
crossover cable
console cable
30.
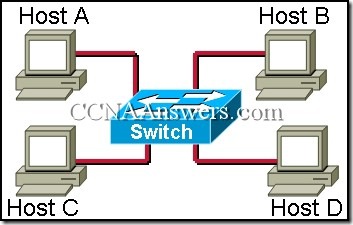
Based on the graphic above, which of the following occurs as each host system comes on line in the topology?
The switch sends its MAC address to each host.
The switch adds MAC address to the bridge table as each host sends a frame.
Each host exchanges MAC addresses with each other.
The switch listens for data traffic to block since the switch lacks an IP address.
31. Two peer hosts are exchanging data using TFTP. During the current session, a datagram fails to arrive at the destination. Which statement is true regarding the retransmission of the datagram?
Datagram retransmission requires user authentication.
Datagram retransmission is controlled by the application.
Datagram retransmission relies on the acknowledgements at transport layer.
Datagram retransmission occurs when the retransmission timer expires in the source host.
32. Which type of address is 192.168.170.112/28?
host address
subnetwork address
broadcast address
multicast address
33. How does a switch learn the addresses of hosts connected to its ports?
All source MAC addresses must be manually configured in CAM.
The switch reads the source MAC address on incoming frames and records it in CAM.
The switch reads the destination MAC address on incoming frames and records it in CAM.
If a switch port is full duplex, the switch reads both the source and destination MAC addresses on incoming frames and records them in CAM.
34. Which protocols are TCP/IP application layer protocols? (Choose two.)
TFTP
IP
TCP
UDP
DNS
35.
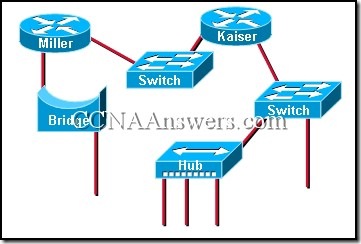
Refer to the exhibit. How many broadcast domains are shown?
three
four
five
six
eight
ten
36.

Refer to the exhibit. Which type of UTP cable should be used to connect Host A to Switch1?
rollover
console
crossover
straight-through
37. A user initiates three simultaneous FTP connections from the local host to the same FTP server. Which OSI layer is responsible for establishing and managing these different FTP connections?
application
session
transport
network
data link
38.
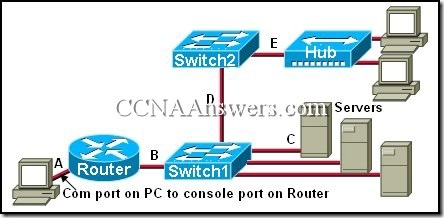
In the exhibit, the connections between the devices are labeled A, B, C, D, and E. For each connection, what is the correct UTP cable to use?
A=straight, B=rollover, C=straight, D=crossover, E=crossover
A=rollover, B=crossover, C=crossover, D=straight, E=straight
A=rollover, B=straight, C=straight, D=crossover, E=straight
A=rollover, B=straight, C=straight, D=crossover, E=crossover
A=straight, B=crossover, C=rollover, D=straight, E=straight
39.
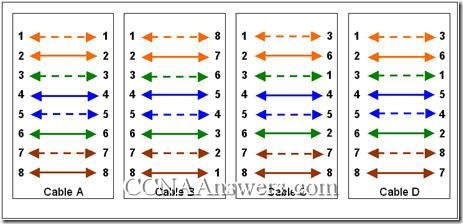
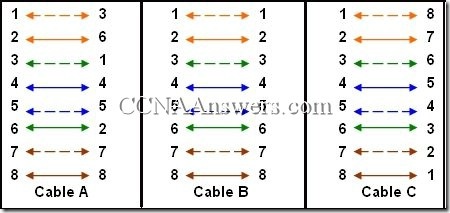
Which cable diagram displays the end to end pinout for a crossover cable used with Cisco devices?
Cable A
Cable B
Cable C
Cable D
40.

Refer to the exhibit. A network associate needs to establish an Ethernet connection between Host A and Host B. However, the distance between the two hosts is further than the cabling standards allow. Which two devices that operate at the physical layer of the OSI can be used to allow Host A and Host B to communicate? (Choose two.)
switch
hub
bridge
router
repeater
41.
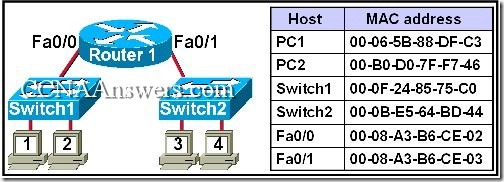
Refer to the exhibit. Workstation 1 pings the Fa0/1 interface of Router 1. Which MAC address will workstation 1 obtain during the ARP request for this communication?
00-06-5B-88-DF-C3
00-B0-D0-7F-F7-46
00-0F-24-85-75-C0
00-0B-E5-64-BD-44
00-08-A3-B6-CE-02
00-08-A3-B6-CE-03
42.

Refer to the exhibit. A network technician is trying to determine the correct IP address configuration for Host A. What is a valid configuration for Host A?
IP address: 192.168.100.19; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248; Default Gateway: 192.16.1.2
IP address: 192.168.100.20; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.17
IP address: 192.168.100.21; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.248; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.18
IP address: 192.168.100.22; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 10.1.1.5
IP address: 192.168.100.30; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.1.1
IP address: 192.168.100.31; Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.240; Default Gateway: 192.168.100.18
43. Which subnet masks could be used when subnetting a Class B IP address? (Choose two.)
255.255.255.240
255.255.192.0
255.255.0.0
255.192.0.0
240.0.0.0
255.0.0.0
44. A network administrator has added a new switch to the network. The new switch connects to an existing switch that is already installed. Which UTP cable correctly connects the new switch to the existing switch?
crossover
rollover
straight-through
console
45.
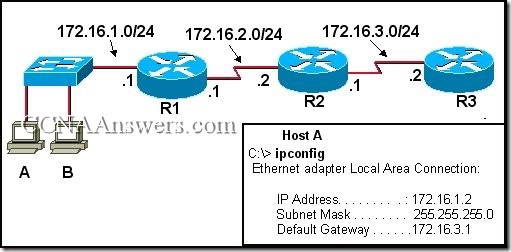
A technician is testing connectivity between the devices using the ping command. Pings between Host B and Host A were successful. The technician could not ping the R3 address 172.16.3.2 from Host A. The technician issued ipconfig from Host A and saw the information displayed in the exhibit. What is the most likely problem?
The IP address of Host A is incorrect.
The subnet mask of Host A is incorrect.
The default gateway of Host A is incorrect.
Host A is properly configured. Some other problem exists in the internetwork.
46. A router interface has been assigned an IP address of 172.16.192.166 with a mask of 255.255.255.248. To which subnet does the IP address belong?
172.16.0.0
172.16.192.0
172.16.192.128
172.16.192.160
172.16.192.168
172.16.192.176
47.
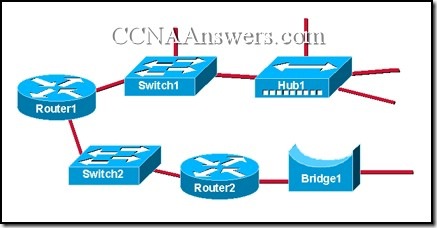
How many collision domains are shown in the diagram?
three
four
five
six
seven
eight
48. A large company has a network that is constantly changing. The routing tables in the routers need to be adjusted to reflect the changes in the routing paths. What type of routing would the network administrator implement?
static routes
dynamic routing protocols
only default routes
none. No routing is necessary.
49.
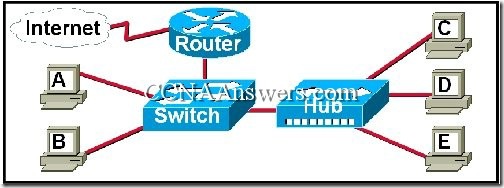
Refer to the exhibit. The hub and the switch are operating using factory default settings. Which hosts will receive the frame if host A transmits a broadcast frame?
Only workstation B and the router will receive the data.
Workstations B, C, D, E, and the router will receive the data.
Only workstations connected to the hub will receive the data.
Workstations B, C, D, E, and the router will receive the data and it will be forwarded into the Internet.


Leave a Reply