CCNA 2 Practice Final Exam Answer V3.1
1. Which statements are true regarding VTY passwords? (Choose two.)
VTY passwords must be encrypted.
All VTY lines do not need to use the same password.
A VTY password is required to establish telnet sessions.
The VTY password is set with the command line console 0.
The VTY password must be identical with the enable secret password.
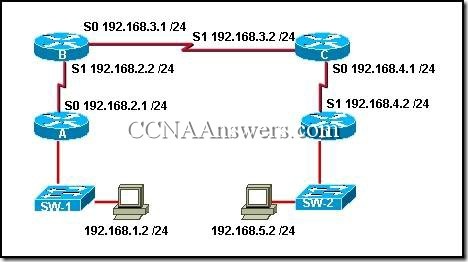
2.
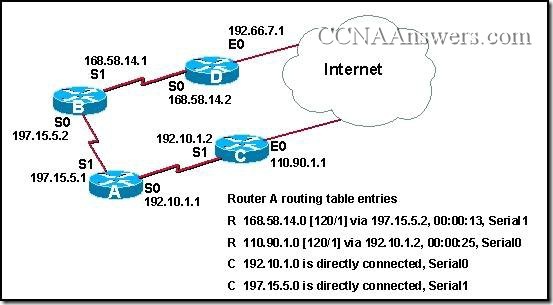
Refer to the network and routing table entries shown in the graphic. What will happen when a packet destined for network 192.66.7.0 is received by Router A?
It will be forwarded through interface S1.
It will be forwarded to the default route.
It will be directed toward the Internet.
It will be discarded.