CCNA 2 Practice Final Exam V4.0 Answers
1.
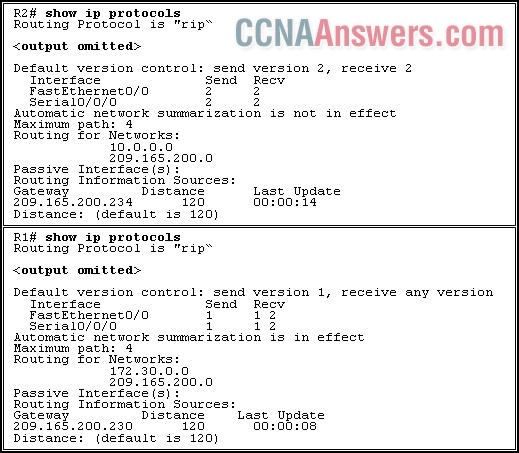
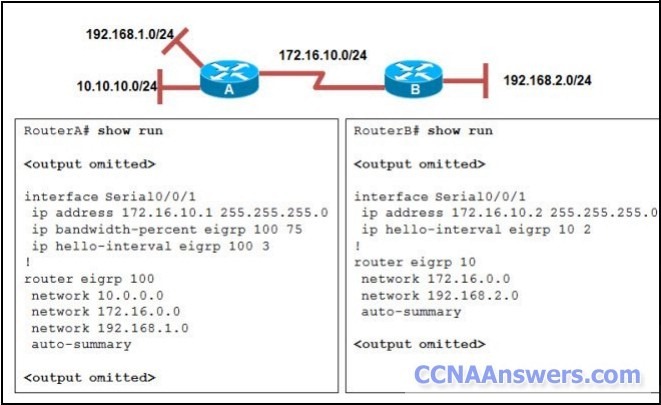
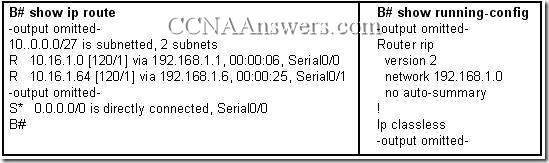
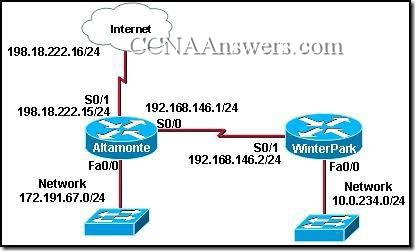
Refer to the exhibit. R1 and R2 are adjacent routers both running RIP. All interfaces on both routers are correctly configured and operational. Both routers are configured to include all connected interfaces in routing updates. R2 is not showing any routes from R1 in the routing table. What is the likely cause?
The adjacent interfaces are passive.
The distance of 120 exceeds 15 hops.
R2 will not accept version 1 updates from R1.
Routes are being summarized by R1 but not by R2.
2.
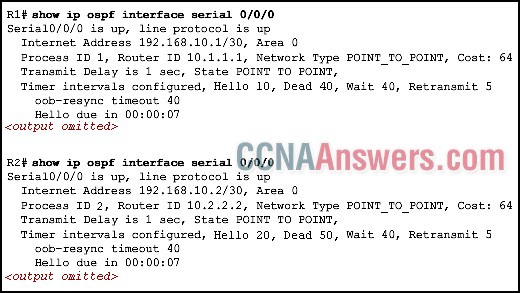
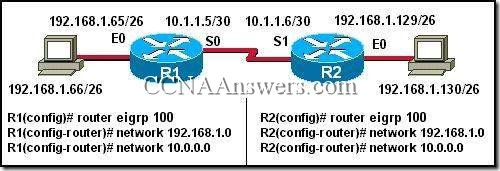
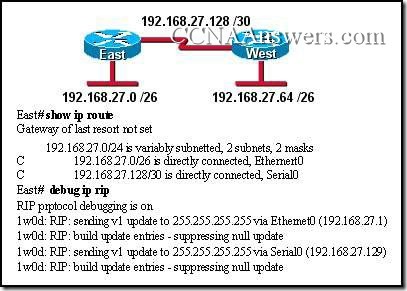
Refer to the exhibit. Two routers are unable to establish an adjacency. What is the possible cause for this?
The two routers are connected on a multiaccess network.
The hello and dead intervals are different on the two routers.
They have different OSPF router IDs.
They have different process IDs.