CCNA 2 Practice Final Exam V4.0 Answers
1.
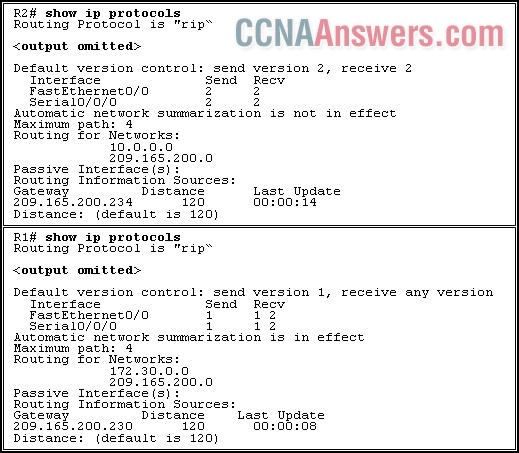
Refer to the exhibit. R1 and R2 are adjacent routers both running RIP. All interfaces on both routers are correctly configured and operational. Both routers are configured to include all connected interfaces in routing updates. R2 is not showing any routes from R1 in the routing table. What is the likely cause?
The adjacent interfaces are passive.
The distance of 120 exceeds 15 hops.
R2 will not accept version 1 updates from R1.
Routes are being summarized by R1 but not by R2.
2.
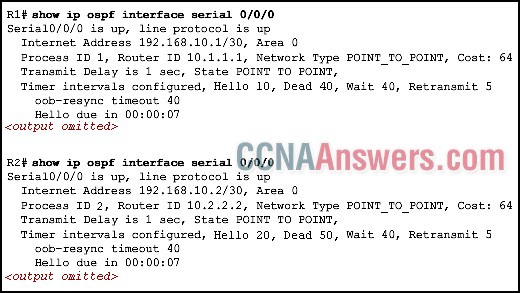
Refer to the exhibit. Two routers are unable to establish an adjacency. What is the possible cause for this?
The two routers are connected on a multiaccess network.
The hello and dead intervals are different on the two routers.
They have different OSPF router IDs.
They have different process IDs.
3. A network is configured with the IP, IPX, and AppleTalk protocols. Which routing protocol is recommended for this network?
RIPv1
RIPv2
EIGRP
OSPF
4.
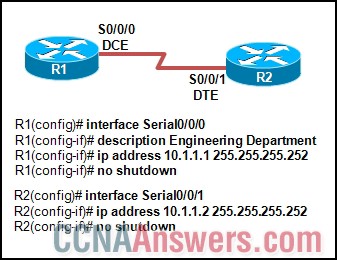
Refer to the exhibit. What needs to be done to allow these two routers to connect successfully?
Add a clock rate to S0/0/0 on R1.
Add an interface description to S0/0/1 on R2.
Change the serial interface on R2 to S0/0/0 so that it matches R1.
Change the IP address of S0/0/1 on R2 so that it is in the same subnet as R1.
5. A router has EIGRP configured as the only routing protocol. In what way might EIGRP respond if there is no feasible successor route to a destination network and the successor route fails?
It broadcasts hello packets to all routers in the network to re-establish neighbor adjacencies.
It sends queries to adjacent neighbors until a new successor route is found.
It immediately sends its entire routing table to its neighbors.
It will set the metric for the failed route to infinity.
6.
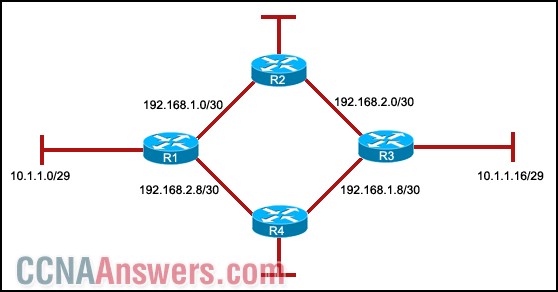
Refer to the exhibit. All routers are running RIPv1. The two networks 10.1.1.0/29 and 10.1.1.16/29 are unable to access each other. What can be the cause of this problem?
Because RIPv1 is a classless protocol, it does not support this access.
RIPv1 does not support discontiguous networks.
RIPv1 does not support load balancing.
RIPv1 does not support automatic summarization.
7. Which port should a terminal emulator be connected to in order to access a router without network connectivity?
T1
serial
console
FastEthernet
8.
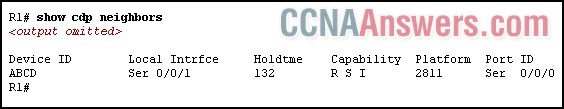
Refer to the exhibit. The show cdp neighbors command was run at R1. Which two facts about the newly detected device can be determined from the output? (Choose two.)
ABCD is a router that is connected to R1.
ABCD is a non-CISCO device that is connected to R1.
The device is connected at the Serial0/0/1 interface of R1.
R1 is connected at the S0/0/1 interface of device ABCD.
9. What is the advantage of configuring a static route with an exit interface instead of a next-hop address?
The router will perform a recursive lookup.
This route will automatically be used as the gateway of last resort.
The exit interface configuration consumes less router processing time.
The exit interface configuration has an administrative distance value of 1.
10.
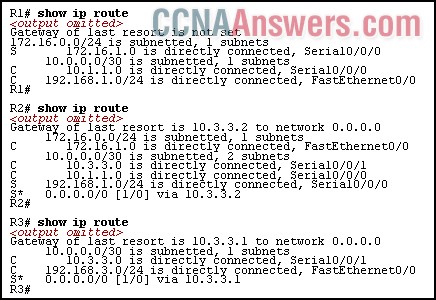
Refer to the exhibit. The network has three connected routers: R1, R2, and R3. The routes of all three routers are displayed. All routers are operational and pings are not blocked on this network.
Which ping will fail?
from R1 to 172.16.1.1
from R1 to 192.168.3.1
from R2 to 192.168.1.1
from R2 to 192.168.3.1
11. What are two advantages of using a loopback interface on a router with OSPF enabled? (Choose two.)
A loopback interface has a much lower OSPF cost value by default.
A loopback interface provides a stable ID because the loopback interface cannot be shutdown.
A network administrator has more control over the DR/BDR election by using a loopback interface over a physical interface.
A loopback interface can be configured with a higher bandwidth value than can a physical interface.
The loopback interface address overrides any physical interface address or configured router-id value.
12.
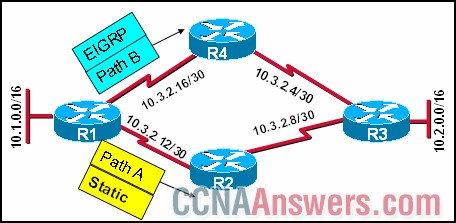
Refer to the exhibit. R1 knows two routes, Path A and Path B, to the Ethernet network attached to R3. R1 learned Path A to network 10.2.0.0/16 from a static route and Path B to network 10.2.0.0/16 from EIGRP. Which route will R1 install in its routing table?
Both routes are installed and load balancing occurs across both paths.
The route via Path B is installed because the EIGRP route has the best metric to network 10.2.0.0/16.
The route via Path A is installed because the static route has the best metric to network 10.2.0.0/16.
The route via Path B is installed because the EIGRP route has the lowest administrative distance to network 10.2.0.0/16.
The route via Path A is installed because the static route has the lowest administrative distance to network 10.2.0.0/16.
13.
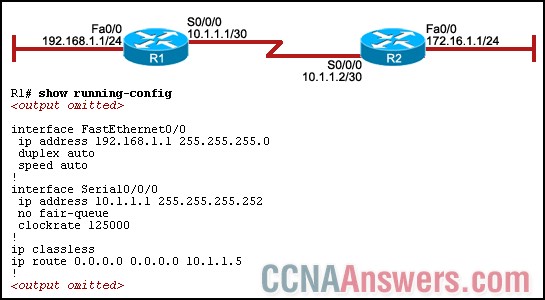
Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has configured R1 as shown, and all interfaces are functioning correctly. A ping from R1 to 172.16.1.1 fails. What could be the cause of this problem?
The serial interface on R1 is configured incorrectly.
The default route is configured incorrectly.
The default-information originate command must be issued on R1.
Autosummarization must be disabled on R1.
14.
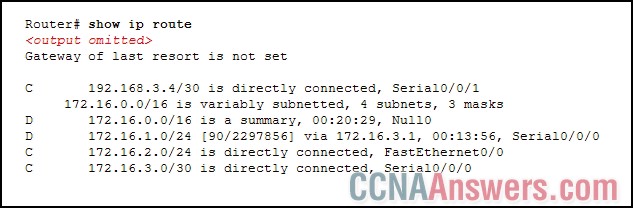
Refer to the exhibit. What happens to a packet that has 172.16.0.0/16 as the best match in the routing table that is shown?
The packet is discarded.
The packet is flooded out all interfaces.
The packet is forwarded via Serial0/0/0.
The packet is forwarded via FastEthernet0/0.
15.
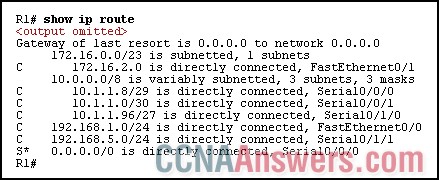
Refer to the exhibit. How many routes are child routes?
1
3
4
6



Leave a Reply