CCNA 3 Chapter 8 V6.0 Answers
1. What happens immediately after two OSPF routers have exchanged hello packets and have formed a neighbor adjacency?
They exchange DBD packets in order to advertise parameters such as hello and dead intervals.
They negotiate the election process if they are on a multiaccess network.
They request more information about their databases.
They exchange abbreviated lists of their LSDBs.
2. What is used to create the OSPF neighbor table?
link-state database
adjacency database
routing table
forwarding database
3. What does a Cisco router use automatically to create link-local addresses on serial interfaces when OSPFv3 is implemented?
an Ethernet interface MAC address available on the router, the FE80::/10 prefix, and the EUI-64 process
the FE80::/10 prefix and the EUI-48 process
the MAC address of the serial interface, the FE80::/10 prefix, and the EUI-64 process
the highest MAC address available on the router, the FE80::/10 prefix, and the EUI-48 process
4. Which command will verify that a router that is running OSPFv3 has formed an adjacency with other routers in its OSPF area?
Show ipv6 route ospf
show running-configuration
show ipv6 interface brief
show ipv6 ospf neighbor
5. Match the information to the command that is used to obtain the information. (Not all options are used.)
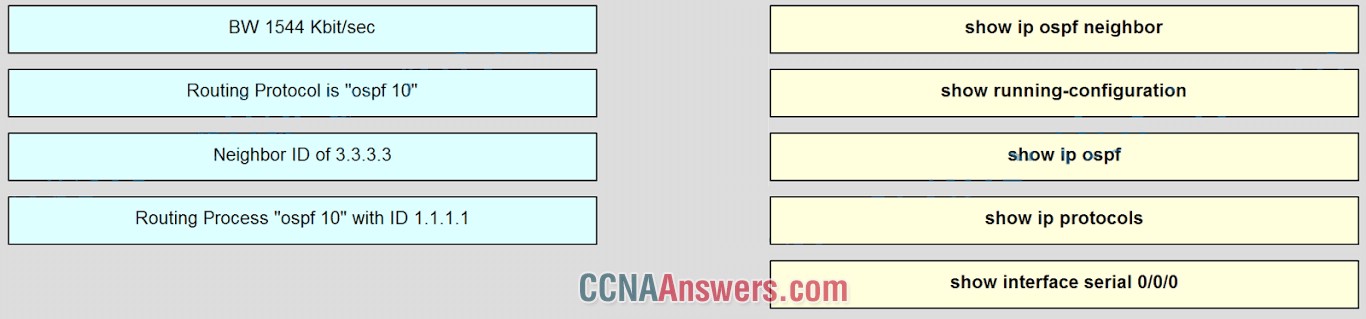
show ip ospf neighbor = Neighbor ID of 3.3.3.3
show ip ospf = Routing Process “ospf 10” with ID 1.1.1.1
show ip protocols = Routing Protocol is "ospf 10"
show interface serial 0/0/0 = BW 1544 Kbit/sec
6. Which three addresses could be used as the destination address for OSPFv3 messages? (Choose three.)
FF02::A
FF02::1:2
FF02::5
FF02::6
FE80::1
2001:db8:cafe::1
7. Which OPSF packet contains the different types of link-state advertisements?
LSAck
LSR
LSU
hello
DBD
8. Match the OSPF state with the order in which it occurs. (Not all options are used.)
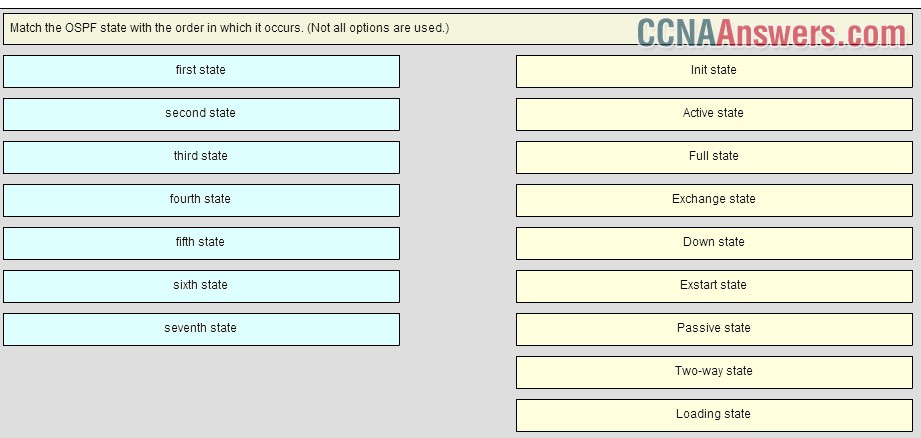
Place the options in the following order:
second state -> Init state
seventh state -> Full state
fifth state -> Exchange state
first state -> Down state
fourth state -> Exstart state
third state -> Two-way state
sixth state -> Loading state
9. Match each OSPF packet type to how it is used by a router. (Not all options are used.)

establish and maintain adjacencies = hello packet
advertise new information = link-state update packet
compare local topology to that sent by another router = database description packet
query another router for additional information = link-state request packet
10. By default, what is the OSPF cost for any link with a bandwidth of 100 Mb/s or greater?
1
100
100000000
10000
11. Fill in the blank.The election of a DR and a BDR takes place on _multiaccess_ networks, such as Ethernet networks.
12. By order of precedence, match the selection of router ID for an OSPF-enable router to the possible router ID options. (Not all option are used.)

loopback interface address 10.1.1.1 = Third precedence
Serial interface IP address 192.168.10.1 = Fourth precedence
Configured router ID 1.1.1.1 = First precedence
Loopback interface IP address 172.16.1.1 = Second precedence
13. Which command should be used to check the OSPF process ID, the router ID, networks the router is advertising, the neighbors the router is receiving updates from, and the default administrative distance?
show ip ospf neighbor
show ip ospf interface
show ip protocols
show ip ospf
14. What are two reasons that will prevent two routers from forming an OSPFv2 adjacency? (Choose two.)
mismatched subnet masks on the link interfaces
use of private IP addresses on the link interfaces
mismatched OSPF Hello or Dead timers
one router connecting to a FastEthernet port on the switch and the other connecting to a GigabitEthernet port
a mismatched Cisco IOS version that is used
15. Which command will provide information specific to OSPFv3 routes in the routing table?
show ipv6 route
show ipv6 route ospf
show ip route ospf
show ip route
16. Single area OSPFv3 has been enabled on a router via the ipv6 router ospf 20 command. Which command will enable this OSPFv3 process on an interface of that router?
ipv6 ospf 20 area 20
ipv6 ospf 20 area 0
ipv6 ospf 0 area 0
ipv6 ospf 0 area 20
17. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question. R1 and R2 could not establish an EIGRP adjacency. What is the problem?
EIGRP is down on R1.
EIGRP is down on R2.
R1 Fa0/0 and R2 Fa0/0 are on different networks.
R1 Fa0/0 is not configured to send hello packets.
R1 Fa0/0 link local address is wrong.
18. When a network engineer is configuring OSPFv3 on a router, which command would the engineer issue immediately before configuring the router ID?
clear ipv6 ospf process
interface serial 0/0/1
ipv6 router ospf 10
ipv6 ospf 10 area 0
19. Fill in the blank.
OSPF uses _cost_ as a metric.
20. What are the two purposes of an OSPF router ID? (Choose two.)
to uniquely identify the router within the OSPF domain
to facilitate the transition of the OSPF neighbor state to Full
to facilitate the establishment of network convergence
to enable the SPF algorithm to determine the lowest cost path to remote networks
to facilitate router participation in the election of the designated router
21. Which OSPF component is identical in all routers in an OSPF area after convergence?
SPF tree
adjacency database
link-state database
routing table
22. What will an OSPF router prefer to use first as a router ID?
the highest active interface IP that is configured on the router
any IP address that is configured using the router-id command
the highest active interface that participates in the routing process because of a specifically configured network statement
a loopback interface that is configured with the highest IP address on the router
23. A network administrator enters the command ipv6 router ospf 64 in global configuration mode. What is the result of this command?
The reference bandwidth will be set to 64 Mb/s.
The router will be assigned an autonomous system number of 64.
The OSPFv3 process will be assigned an ID of 64.
The router will be assigned a router ID of 64.


Leave a Reply