CCNA 1 Chapter 9 V6.0 Answers
1. Which two flags in the TCP header are used in a TCP three-way handshake to establish connectivity between two network devices? (Choose two.)
SYN
FIN
PSH
URG
RST
ACK
2. What happens if part of an FTP message is not delivered to the destination?
The message is lost because FTP does not use a reliable delivery method.
The FTP source host sends a query to the destination host.
The entire FTP message is re-sent.
The part of the FTP message that was lost is re-sent.
3. What kind of port must be requested from IANA in order to be used with a specific application?
dynamic port
registered port
private port
source port
4. When is UDP preferred to TCP?
when a client sends a segment to a server
when segments must arrive in a very specific sequence to be processed successfully
when an application can tolerate some loss of data during transmission
when all the data must be fully received before any part of it is considered useful
5. Which two characteristics are associated with UDP sessions? (Choose two.)
Received data is unacknowledged.
Destination devices reassemble messages and pass them to an application.
Unacknowledged data packets are retransmitted.
Transmitted data segments are tracked.
Destination devices receive traffic with minimal delay.
6. A host device needs to send a large video file across the network while providing data communication to other users. Which feature will allow different communication streams to occur at the same time, without having a single data stream using all available bandwidth?
multiplexing
window size
port numbers
acknowledgments
7. What happens if the first packet of a TFTP transfer is lost?
The TFTP application will retry the request if a reply is not received.
The client will wait indefinitely for the reply.
The transport layer will retry the query if a reply is not received.
The next-hop router or the default gateway will provide a reply with an error code.
8. What does a client do when it has UDP datagrams to send?
It just sends the datagrams.
It sends a simplified three-way handshake to the server.
It queries the server to see if it is ready to receive data.
It sends to the server a segment with the SYN flag set to synchronize the conversation.
9. What is a characteristic of UDP?
UDP datagrams take the same path and arrive in the correct order at the destination.
Applications that use UDP are always considered unreliable.
UDP only passes data to the network when the destination is ready to receive the data.
UDP reassembles the received datagrams in the order they were received.
10. A host device is receiving live streaming video. How does the device account for video data that is lost during transmission?
The device will use sequence numbers to pause the video stream until the correct data arrives.
The device will continue receiving the streaming video, but there may be a momentary disruption.
The device will delay the streaming video until the entire video stream is received.
The device will immediately request a retransmission of the missing data.
11. What is the complete range of TCP and UDP well-known ports?
1024 – 49151
256 – 1023
0 to 255
0 to 1023
12. Which flag in the TCP header is used in response to a received FIN in order to terminate connectivity between two network devices?
FIN
RST
ACK
SYN
13. During a TCP session, a destination device sends an acknowledgment number to the source device. What does the acknowledgment number represent?
The last sequence number that was sent by the source
one number more than the sequence number
the total number of bytes that have been received
the next byte that the destination expects to receive
14. What is a characteristic of a TCP server process?
Every application process running on the server has to be configured to use a dynamic port number.
There can be many ports open simultaneously on a server, one for each active server application.
A host running two different applications can have both configured to use the same server port.
An individual server can have two services assigned to the same port number within the same transport layer services.
15. Which three application layer protocols use TCP? (Choose three.)
SMTP
DHCP
HTTP
FTP
SNMP
TFTP
16. Refer to the exhibit. Consider a datagram that originates on the PC and that is destined for the web server. Match the IP addresses and port numbers that are in that datagram to the description. (Not all options are used.)
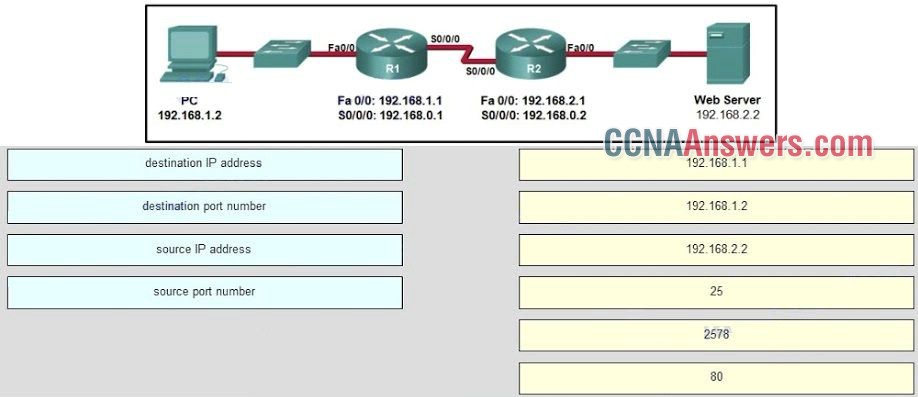
destination IP address -> 192.168.2.2
destination port number -> 80
source IP address -> 192.168.1.2
source port number -> 2578
17. Why does HTTP use TCP as the transport layer protocol?
because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
because HTTP requires reliable delivery
to ensure the fastest possible download speed
18. What does TCP do if the sending source detects network congestion on the path to the destination?
The destination will request retransmission of the entire message.
The source host will send a request for more frequent acknowledgments to the destination.
The source will acknowledge the last segment that is sent and include a request for a smaller window size in the message.
The source will decrease the amount of data that it sends before it must receive acknowledgements from the destination.
19. A PC is downloading a large file from a server. The TCP window is 1000 bytes. The server is sending the file using 100-byte segments. How many segments will the server send before it requires an acknowledgment from the PC?
10 segments
100 segments
1000 segments
1 segment
20. What information is used by TCP to reassemble and reorder received segments?
fragment numbers
acknowledgment numbers
port numbers
sequence numbers
21. What type of information is included in the transport header?
destination and source port numbers
destination and source logical addresses
encoded application data
destination and source physical addresses
22. What is a socket?
the combination of the source and destination sequence numbers and port numbers
the combination of a source IP address and port number or a destination IP address and port number
the combination of the source and destination IP address and source and destination Ethernet address
the combination of the source and destination sequence and acknowledgment numbers
23. Which factor determines TCP window size?
the number of services included in the TCP segment
the amount of data to be transmitted
the amount of data the destination can process at one time
the amount of data the source is capable of sending at one time


Leave a Reply