CCNA 1 Chapter 7 V5.0 Answers
1. A host device sends a data packet to a web server via the HTTP protocol. What is used by the transport layer to pass the data stream to the proper application on the server?
sequence number
acknowledgment
source port number
destination port number
2. What does a client application select for a TCP or UDP source port number?
a random value in the well-known port range
a random value in the range of the registered ports
a predefined value in the well-known port range
a predefined value in the range of the registered ports
3. What is a socket?
the combination of the source and destination IP address and source and destination Ethernet address
the combination of a source IP address and port number or a destination IP address and port number
the combination of the source and destination sequence and acknowledgment numbers
the combination of the source and destination sequence numbers and port numbers
4. Which two flags in the TCP header are used in a TCP three-way handshake to establish connectivity between two network devices? (Choose two.)
ACK
FIN
PSH
RST
SYN
URG
5. Fill in the blank using a number.
A total of ...4...messages are exchanged during the TCP session termination process between the client and the server.
6. What is a beneficial feature of the UDP transport protocol?
acknowledgment of received data
fewer delays in transmission
tracking of data segments using sequence numbers
the ability to retransmit lost data
7. A host device needs to send a large video file across the network while providing data communication to other users. Which feature will allow different communication streams to occur at the same time, without having a single data stream using all available bandwidth?
window size
multiplexing
port numbers
acknowledgments
8. Fill in the blank.
During a TCP session, the...SYN...flag is used by the client to request communication with the server.
9.
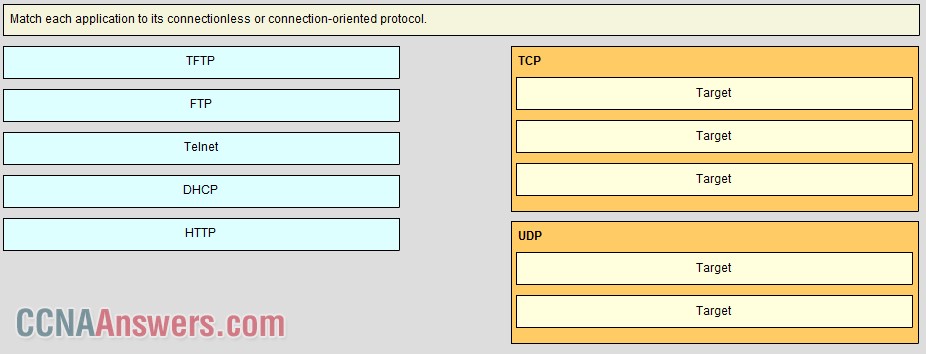
10. A PC is downloading a large file from a server. The TCP window is 1000 bytes. The server is sending the file using 100-byte segments. How many segments will the server send before it requires an acknowledgment from the PC?
1 segment
10 segments
100 segments
1000 segments
11. Which transport layer feature is used to guarantee session establishment?
UDP ACK flag
TCP 3-way handshake
UDP sequence number
TCP port number
12. During a TCP session, a destination device sends an acknowledgment number to the source device. What does the acknowledgment number represent?
the total number of bytes that have been received
one number more than the sequence number
the next byte that the destination expects to receive
the last sequence number that was sent by the source
13. Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
14. A technician wishes to use TFTP to transfer a large file from a file server to a remote router. Which statement is correct about this scenario?
The file is segmented and then reassembled in the correct order by TCP.
The file is segmented and then reassembled in the correct order at the destination, if necessary, by the upper-layer protocol.
The file is not segmented, because UDP is the transport layer protocol that is used by TFTP.
Large files must be sent by FTP not TFTP.
15.
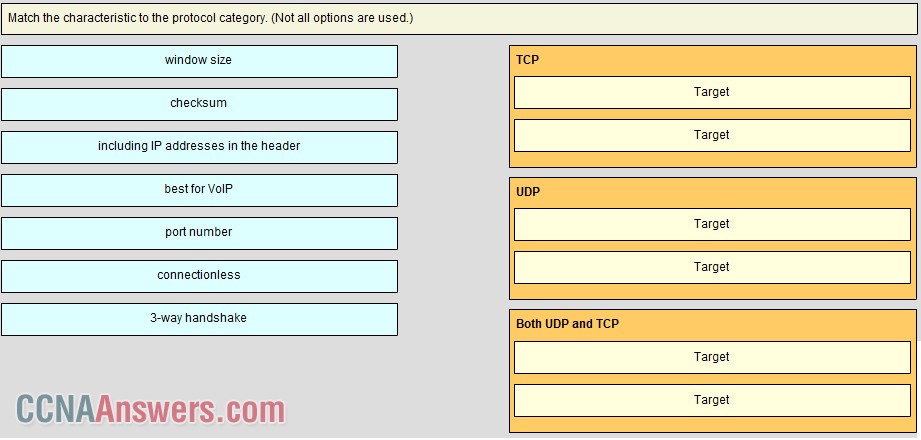
TCP uses 3-way handshaking as part of being able to provide reliable communication and window size to provide data flow control. UDP is a connectionless protocol that is great for video conferencing. Both TCP and UDP have port numbers to distinguish between applications and application windows and a checksum field for error detection.
16.
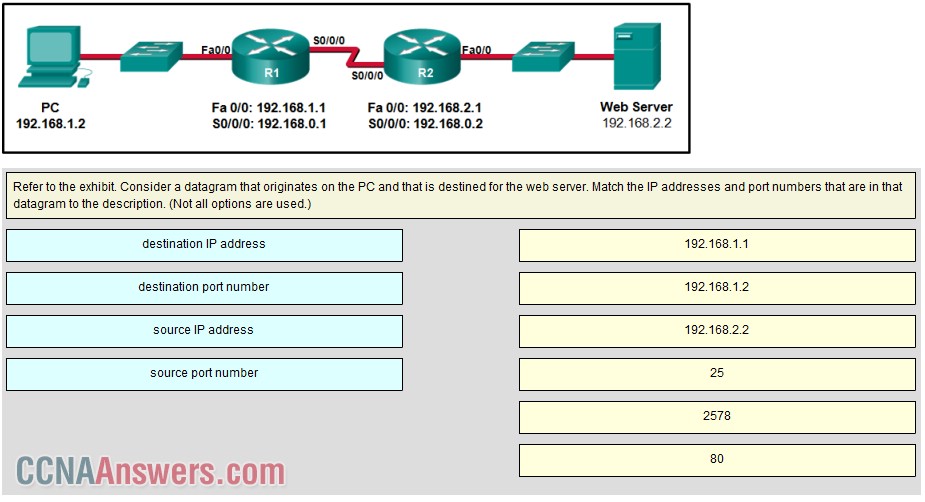
A TCP/IP segment that originated on the PC has 192.168.1.2 as the IP source address. 2578 is the only possible option for the source port number because the PC port number must be in the range of registered ports 1024 to 49151. The destination is the web server, which has the IP address 192.168.2.2, and the destination port number is 80 according to the HTTP protocol standard.
17. Which factor determines TCP window size?
the amount of data to be transmitted
the number of services included in the TCP segment
the amount of data the destination can process at one time
the amount of data the source is capable of sending at one time
18. Which two TCP header fields are used to confirm receipt of data?
FIN flag
SYN flag
checksum
sequence number
acknowledgment number
19. What happens if the first packet of a TFTP transfer is lost?
The client will wait indefinitely for the reply.
The TFTP application will retry the request if a reply is not received.
The next-hop router or the default gateway will provide a reply with an error code.
The transport layer will retry the query if a reply is not received.
20. What does a client do when it has UDP datagrams to send?
It just sends the datagrams.
It queries the server to see if it is ready to receive data.
It sends a simplified three-way handshake to the server.
It sends to the server a segment with the SYN flag set to synchronize the conversation.
21. What is the complete range of TCP and UDP well-known ports?
0 to 255
0 to 1023
256 - 1023
1024 - 49151
22. Compared to UDP, what factor causes additional network overhead for TCP communication?
network traffic that is caused by retransmissions
the identification of applications based on destination port numbers
the encapsulation into IP packets
the checksum error detection




Leave a Reply